Analysis of Descemet Membrane Detachment
After DMEK Surgery
Ella Sahar, Yahel Oren
Advisor: Dr. Yair Zimmer
Client: Department of Ophthalmology in Rabin Medical Center
Medical Engineering
Following is a schematic block diagram of the algorithm:
The developed GUI enables the user to upload a set of OCT images and be able to see
the detachment area of each cross-section, and to observe the total volume and its
value.
Results:
The area algorithm was tested on 31 images, 21 of them belong to a set of images for
which the volume algorithm was tested as well.
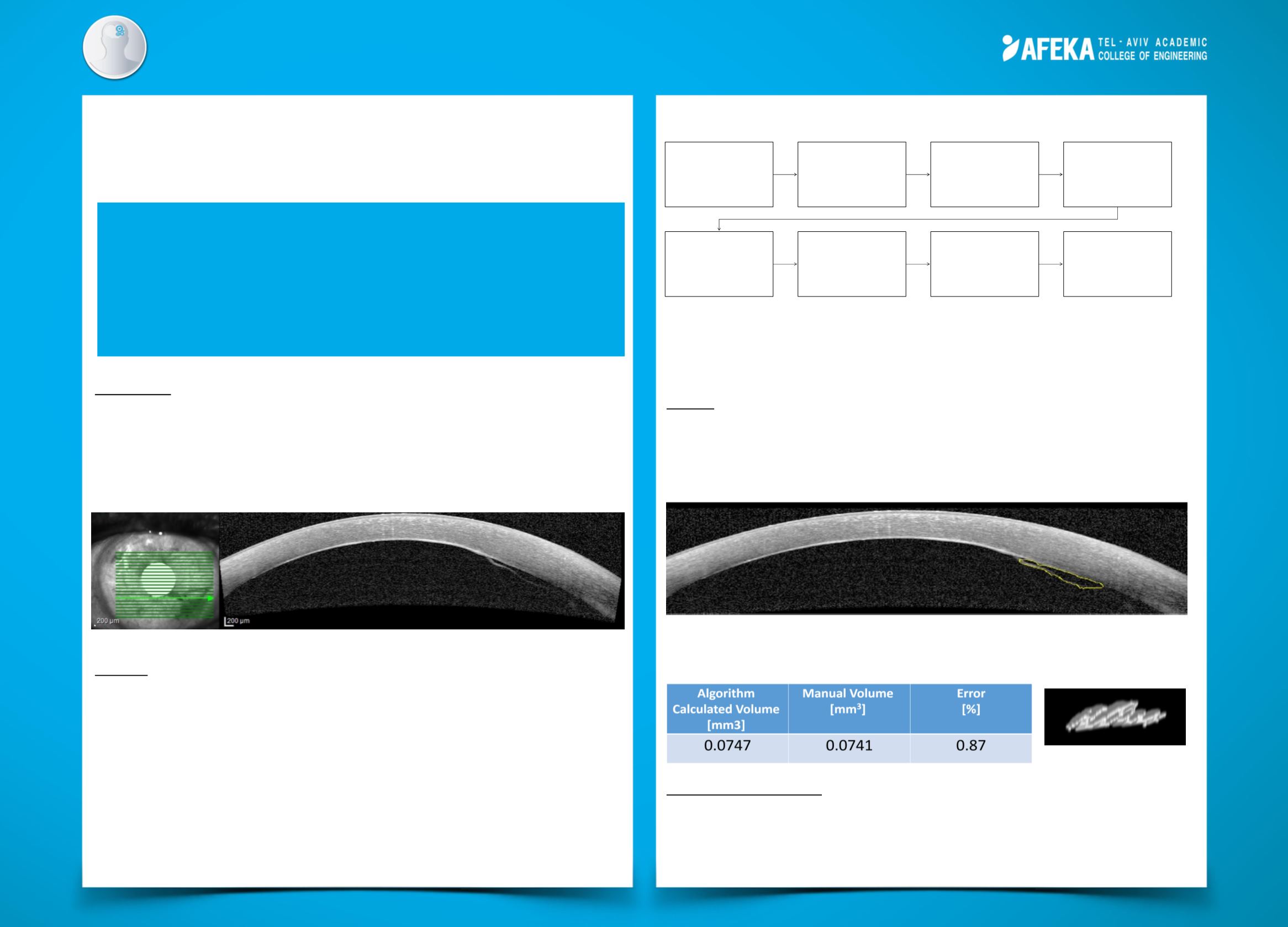
The automatic algorithm results were compared the to manual tracing approved by an
ophthalmologist. An example of the algorithm area recognition is shown below.
The mean error of the area calculation for 31 tested images is 12.49%. The following
table describes the volume result and error calculation, and the figure below is the
volume in a 3-D graphic display.
Discussion and Summary:
The primary goal of the project was to develop an automatic tool to detect and measure
the area and volume created by graft dislocation. This goal was achieved in 90.3% for
area calculation and the volume calculation accuracy was more than 99%. In addition, a
GUI was created in order to supply the ophthalmologist an accessible tool.
Background:
Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK) is a surgery aimed to replace a
thin layer of the cornea in order to reconstruct a person's vision. This layer might be
detached after surgery and in order to relocate it, a small volume of air is inserted into
the human eye, a process that is called re-bubbling. Currently there is no algorithm that
calculates the volume of the detachment and the ophthalmologists need to evaluate the
volume by inaccurate techniques.
Method:
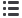
Image acquisition was performed using SPECTRALIS® Heidelberg Engineering by Rabin
Medical Center for patients that underwent DMEK surgery. An example of an OCT B-Scan
and a grid that indicates the image’s location in the set is shown above.
The algorithm developed in the project includes segmentation (using Chan-Vese and
Otsu methods), noise reduction, morphological filtering, contrast enhancement (Frangi
filtering) and other image processing tools.
In this project, a tool for ophthalmologists that analyzes OCT
images taken after DMEK surgery was developed. Images
were processed by an image processing algorithm which
calculates the area formed by graft detachment, all areas
are integrated to determine the volume formed by the
detachment. A GUI was designed to analyze images easily.
Image
acquisition
(full series)
Cornea
reconstruction
Extraction of
the cornea's
lower line
Extraction of
the detachment
Reconstructing
the detachment's
surrounding
Continuation of
the detachment
Extracting the
area formed by
the detachment
Integrate to a
volume
structure